Precalculus for Everybody
Equation Graphs. Symmetry and Translations
In the exercises, from 1 to 7, use the test of symmetry to determine if the graph of the equation is symmetric with respect to the X-axis, Y-axis or the origin.
-
\[ y = x^2 \]
-
\[ xy = 1 \]
-
\[ \frac{x^2}{4} + \frac{y^2}{9} = 1 \]
-
\[ \frac{x^2}{4} - \frac{y^2}{9} = 1 \]
-
\[ y^2(2 - x) = x^3 \]
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 + x = \sqrt{x^2+y^2} \]
-
\[ (x^2 + y^2)^2 = x^2 - y^2 \]
In the exercises, from 8 to 16, find an equation of the circle satisfying the given conditions.
- Center, \((2, -1)\); \(r = 5\).
- Center \((-3, 2)\); \(r =\sqrt{5}\).
- Center in the origin, pass through \((-3, 4)\).
- Center \((1, -1)\), pasa por \((6, 4)\).
- Center \((1, -3)\), es tangente al eje X.
- Center \((-4, 1)\), es tangente al eje Y.
- A diameter with endpoints: \((2, 4)\) and \((4, -2)\).
- Radius \(r = 1\) pass through: \((1, 1)\) and \((1, -1)\).
- Passing through the points \((0, 0)\), \((0, 8)\) and \((6, 0)\).
In the exercises, from 17 to 22, prove that the equation corresponds to a circle by finding the center and the radius.
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 - 2x - 3 = 0 \]
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 + 4y - 4 = 0 \]
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 + y = 0 \]
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 - 2x + 4y - 4 = 0 \]
-
\[ 2x^2 + 2y^2 - x + y - 1 = 0 \]
-
\[ 16x^2 + 16y^2 - 48x - 16y - 41 = 0 \]
In the exercises 23, 24 and 25 use the translation criterion on the semi-cubical parabola(ex. 2.2.7-b) to graph the equations.
-
\[ (y - 1)^2 = (x + 1)^3 \]
-
\[ (x - 1)^2 = (y + 1)^3 \]
-
\[ (y+1)^2 = (x - 1)^3 \]
In the exercises, from 26 to 28, graph the equation. Use the translation and inversion criteria, and the graph of the Agnesi witch (example 2.2.7-a).
-
\[ (x-3)^2(y-2)=4(4-y) \]
-
\[ (y - 3)^2(x - 2) = 4(4 - x) \]
-
\[ (x + 3)^2(y + 2) = 4(-y) \]
Answers
- Y-axis
- Origin
- X-axis, Y-axis and Origin
- X-axis, Y-axis and Origin
- X-axis
- X-axis
- X-axis, Y-axis and Origin
-
\[ (x – 2)^2 + (y + 1)^2 = 25 \]
-
\[ (x + 3)^2 + (y – 2)^2 = 5 \]
-
\[ x^2 + y^2 = 25 \]
-
\[ (x – 1)^2 + (y + 1)^2 = 50 \]
-
\[ (x – 1)^2 + (y + 3)^2 = 9 \]
-
\[ (x + 4)^2 + (y – 1)^2 = 16 \]
-
\[ (x – 3)^2 + (y – 1)^2 = 10 \]
-
\[ (x – 1)^2 + y^2 = 1 \]
-
\[ (x – 3)^2 + (y – 4)^2 = 25 \]
- Center \((1, \, 0), \; r= 2\)
- Center \((0, \, -2), \; r = 2 \sqrt{2}\)
- Center \(\left( 0, \, -\frac{1}{2} \right), \; r = \frac{1}{2} \)
- Center \((1, \, -2), \; r = 3\)
- Center \(\left( \frac{1}{4}, \, -\frac{1}{4} \right), \; r = \frac {\sqrt{10}}{4}\)
- Center \(\left( \frac{3}{2}, \, \frac{1}{2} \right), \; r = \frac{9}{4}\)
-
\[ (y – 1)^2 = (x + 1)^3 \]

-
\[ (x – 1)^2 = (y + 1)^3 \]
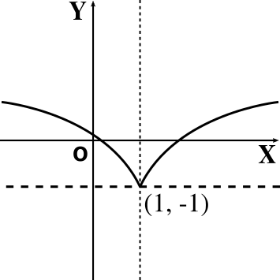
-
\[ (y + 1)^2 = (x – 1)^3 \]

-
\[ (x-3)^2 (y – 2) = 4 \left(2 -(y – 2) \right) \]
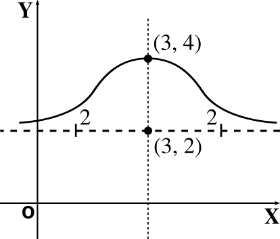
-
\[ (y – 3)^2 (x – 2)= 4 \left( 2 – (x-2) \right) \]

-
\[ (x + 3)^2 (y + 2) = 4 \left( 2 -(y + 2) \right) \]

